Title: Unveiling the Mystery: What Configuration is Keratin?
Meta Description: Curious about the configuration of keratin? Delve into this comprehensive article to uncover the secrets behind the structure of keratin, its importance, and its role in various aspects of our lives.
Introduction
Keratin is a structural protein found in various parts of our body, such as hair, skin, nails, and even the outermost layer of our epidermis. It plays a crucial role in providing strength, rigidity, and protection to these tissues. But have you ever wondered what configuration is keratin and how it contributes to its unique properties? In this article, we will explore the intricate structure of keratin and shed light on its significance.
Understanding the Configuration of Keratin
1. The Primary Structure
The primary structure of keratin is determined by its amino acid sequence, which is encoded by our DNA. This sequence consists of repeating units of amino acids, mainly cysteine, glycine, and serine. These amino acids are responsible for the unique characteristics of keratin, such as its strength and flexibility.
2. The Secondary Structure
Keratin adopts a helical conformation known as the alpha-helix in its secondary structure. This helical structure
What does keratin do in the cell
Title: Unlocking the Wonders of Keratin in Cell Functions
Introduction:
Keratin is a protein found in the cells of various organisms, including humans. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and function of these cells. This brief review aims to highlight the positive aspects and benefits of keratin in cellular functions, while also exploring the conditions where keratin proves beneficial.
I. Structure and Function of Keratin in the Cell:
1. Keratin's primary role is to provide structural support and strength to cells, tissues, and organs.
2. It forms strong filaments that contribute to the integrity and elasticity of various cell types.
3. Keratin acts as a protective barrier against mechanical stress, such as abrasion and stretching.
4. It helps maintain cell shape and stability, ensuring efficient cellular communication and transport processes.
II. Benefits of Keratin in Cell Functions:
1. Tissue Regeneration:
- Keratin promotes the regeneration of damaged tissues by facilitating cell migration and wound healing.
- It accelerates the formation of new cells, contributing to tissue repair and recovery.
2. Epidermal Health:
- Keratin is a key component of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.
- It forms a
Keratin tissue found in what tissue
Title: Keratin Tissue: Its Occurrence and Function in the Human Body
Meta Description: This expert review provides an informative overview of keratin tissue, exploring its presence in various tissues within the human body. Discover the significance of keratin tissue in maintaining the health and functionality of these tissues.
Introduction:
Keratin tissue is a critical component found in various tissues throughout the human body. This review aims to shed light on the occurrence and function of keratin tissue within different regions of the body, highlighting its importance in maintaining tissue health. By understanding the role of keratin in these tissues, we can better appreciate its significance and potential implications for human health.
Keratin Tissue in the Skin:
One of the most well-known functions of keratin tissue is its presence in the skin. Specifically, keratinocytes present in the outermost layer of the skin, known as the epidermis, produce keratin proteins. These proteins provide structural support, strength, and protection to the skin. Keratin tissue in the skin acts as a barrier against external factors, such as pathogens, ultraviolet radiation, and environmental pollutants.
Keratin Tissue in Hair and Nails:
Another prominent area where keratin tissue is found is within hair and nails. Hair consists of
Where cells that have the most keratin can be found?
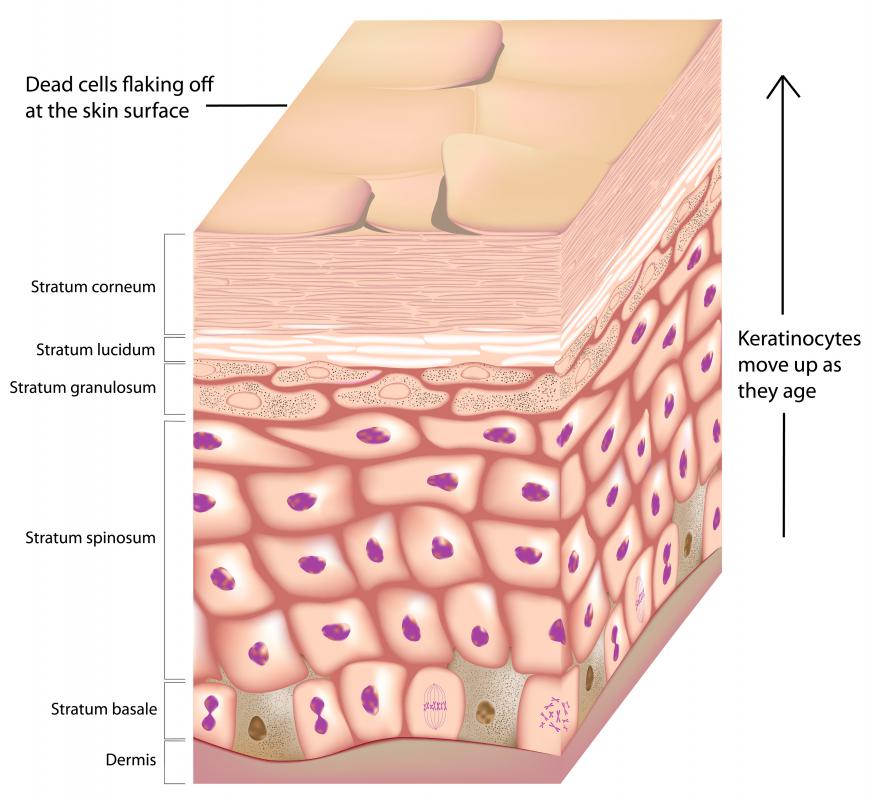
The epidermis layer that has the most keratinized cells is the stratum corneum. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis and serves to protect the inner layers of the epidermis from mechanical damage and desiccation.
What layer is keratin found?
Epidermis layer
Instead, the protein known as keratin is primarily found in the epidermis layer of the skin. Of the layers of the epidermis, keratin is contained in cells called keratinocytes found in the stratum corneum, the outer layer.
Which cell organelle will make keratin?
Ribosomes are the organelles that synthesize proteins, including melanin and keratin.



To answer these questions, Fuchs and her team expressed mutant keratin proteins in mice, finding that when epidermal stem cells lack a proper keratin cytoskeleton, they can’t withstand mechanical trauma.
— Gairdner Foundation (@GairdnerAwards) October 22, 2020
Where is keratin found in?
Where is keratin located? Keratin is in your hair, nails and your skin's outer layer, and it's also in your glands and organs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where does keratin build up?
Keratin plugs can develop anywhere on your body, but they usually appear on your upper arms, thighs and buttocks (bottom). They're more common in children and teenagers. They often get worse around puberty.
Is keratin made in ribosomes?
Keratin is an intracellular protein. It is made by a free ribosome.
What is unique about keratin?
Keratins are found only in epithelial cells and are characterized by unique physicochemical properties (Steinert et al. 1982; Sun et al. 1983). They are resistant to digestion by the proteases pepsin or trypsin and are insoluble in dilute acids, alkalines, water and organic solvents (Block, 1951; Steinert et al. 1982).
What is the biological importance of keratin?
It serves as an energy substrate by contributing to the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate. Creatine has proven effective in enhancing muscle performance during brief, high intensity exercise, but has no effect on longer-duration exercise.
What is the role of keratin in the body?
Keratin is a protein that helps form hair, nails and your skin's outer layer (epidermis). It helps support your skin, heal wounds and keep your nails and hair healthy. There are 54 kinds of keratin in your body.
Is keratin a structural protein?
Keratin, fibrous structural protein of hair, nails, horn, hoofs, wool, feathers, and of the epithelial cells in the outermost layers of the skin. Keratin serves important structural and protective functions, particularly in the epithelium.
What causes the body to produce keratin?
Keratin is a tough, fibrous protein found in fingernails, hair, and skin. The body may produce extra keratin as a result of inflammation, as a protective response to pressure, or as a result of a genetic condition. Most forms of hyperkeratosis are treatable with preventive measures and medication.
What is the content of keratin?
Keratin is the main structural protein that forms the hair, wool, feathers, nails, and horns of many types of animals [83]. The protein has high contents of cysteine (7%–20% of the total amino acid residues), which is known to form intramolecular and intermolecular disulfide bonds [84,85].
What is the function of keratin quizlet?
The function of keratin in the skin is to provide a tough, protective barrier against mechanical stress, physical trauma, and water loss. Keratin is a fibrous protein that is a major component of the outermost layer of the skin, called the epidermis.
What category does keratin belong to?
Fibrous proteins
The correct answer is a) protein. Collagen and keratin belong to the category of proteins. Both collagen and keratin belong to the group of fibrous proteins.
Is keratin a soft tissue?
α-Keratin is usually found in soft tissues like sheep wool, skin, and hair, while β-keratin is found in hard tissues like bird feathers, horns, claws, and hooves [77].
Is keratin a cell or protein?
Keratin is a protein that your body produces naturally, and it helps keep your hair, skin and nails healthy and strong. Your body produces keratin naturally, but keratin shampoos and conditioners that contain keratin hydrolysates may strengthen your hair and improve its appearance.
What type of material is keratin?
Fibrous protein
Keratin is the cysteine-rich fibrous protein that associate with intermediate filaments (IFs) forming the bulk of cytoskeleton and epidermal appendageal structures such as hair, horns, feathers, wool and nails [7].
Is keratin a epithelial tissue?
Keratins are found only in epithelial cells and are characterized by unique physicochemical properties (Steinert et al. 1982; Sun et al. 1983). They are resistant to digestion by the proteases pepsin or trypsin and are insoluble in dilute acids, alkalines, water and organic solvents (Block, 1951; Steinert et al. 1982).
What tissue is keratin found in?
Α-Keratin is usually found in soft tissues like sheep wool, skin, and hair, while β-keratin is found in hard tissues like bird feathers, horns, claws, and hooves [77]. Normally, keratin biomass is subjected to hydrolyzation with acid, alkali, or enzyme to isolate the keratin.
What layer of the epithelial contains that keratin?
Stratum basale (stratum germinativum; pronounced stray-tum bay-say-lee or stray-tum germ-in-a-tie-vum). The stratum basale is in the deepest layer of your epidermis. New skin cells develop in this layer. It also contains the keratinocyte (cur-at-in-o-site) stem cells, which produce the protein keratin.
What are the sources of keratin?
The nutrients in certain foods can boost keratin production in the body, helping to strengthen the skin, hair, and nails. Examples of these foods include eggs, salmon, onion, sweet potato, and more. Keratin is a protein that helps maintain the structure of hair, nails, skin, and the lining of the internal organs.
Is keratin found in connective tissue?
No. Collagen is abundantly found in the ECM and in connective tissues. Keratin is mainly seen in the epithelial cells and in appendages such as feathers, hairs and nail, horn, claws and hooves.
What organelle produces keratin?
Keratinocytes are cells that make up over 90% of the epidermis or the outer layer of the skin. They produce an secrete a protein called “keratin” which is also called an intermediate filament protein, that holds the skin cells and layers together.
Where does keratin come from?
Your body produces keratin naturally. Animal fur, feathers, hooves and horns also consist of keratin. The keratin in keratin hair treatments usually comes from ground-up animal parts, so if you're a vegetarian, you may not want to use these products.
What is keratin made of biology?
Keratin is a fibrous structural protein abundant in hair, nails, skin, feathers, hooves, horns, and so on. Keratins are made up of coiled polypeptide chains and when they combine they form supercoils. Keratins protect epithelial cells from damage.
What type of cell is keratin specialized?
Abstract. Epidermal keratinocytes (skin cells) are highly specialized epithelial cells designed to perform a very specific function, separation of the organism from its environment.
What makes keratin?
Keratin is produced from living skin cells in the body and is found in our glands and the lining of our organs as well. Considered a protective protein, keratin provides resilience and strength to cells from mild trauma that includes rubbing or scratching.
Which of the following is made out of polymers of keratin?
Keratin-based materials consist of crystalline filaments embedded in an amorphous protein matrix. It is the main structural material of hair, feathers, nails, hooves, calluses, scales, horns, claws (McKittrick et al., 2012). Keratin structure is shown in Fig. 1.2.
Is keratin composed of 18 amino acids?
Keratin is composed of 18 amino acids. The most abundant amino acids are: Cysteine, cystine, serine, glutamic acid, glycine, threonine, arginine, valine, leucine and isoleucine. Alpha keratin, fibrous and with a low sulphur content, is the protein we find in the greatest quantity in hair.
Which of the following is composed of keratin?
Hair, fur and feathers are just a few of many specialized structures composed of keratin. Others include nails, beaks, horns, claws, hooves, quills, whiskers, baleen, turtle shell, and scales. These structures form from the epidermis, the top layer of the skin.
What type of protein is present in keratin?
Keratin isn't a single substance. It consists of many different proteins, including various types of keratins, keratin-associated proteins (KFAPs) and enzymes drawn from animal tissues.
What structures are made of keratin?
Keratin, fibrous structural protein of hair, nails, horn, hoofs, wool, feathers, and of the epithelial cells in the outermost layers of the skin.
What is keratin associated with?
Keratin provides support and protection in your body. Your hair, nails and skin rely on the amount of keratin in your body for their overall health. Your glands and organs also contain keratin. Keratin is strong, so it won't dissolve in diluted acids, alkalines, solvents or waters.
What are the 5 functions of keratin?
What are the functions of keratin? Keratin protects epithelial cells, strengthens the skin, strengthens internal organs, controls the growth of epithelial cells, and maintains elasticity in the skin. It also holds epithelial cells together and helps them combat mechanical stress.
Which of the following is an example of keratin?
Keratin, fibrous structural protein of hair, nails, horn, hoofs, wool, feathers, and of the epithelial cells in the outermost layers of the skin.
FAQ
- What are the diseases associated with keratin?
- Cutaneous disorders include epidermolysis bullosa simplex, palmoplantar keratoderma, epidermolytic ichthyosis and pachyonychia congenita. Both clinical and laboratory observations confirm a major role for keratins in maintaining epidermal cell-cell adhesion.
- What elements make up keratin?
- Keratin is a protein found in the cortex. Keratin is composed of 18 amino acids. The most abundant amino acids are: Cysteine, cystine, serine, glutamic acid, glycine, threonine, arginine, valine, leucine and isoleucine.
- What is keratin composed of?
- What is keratin made of? Keratin isn't a single substance. It consists of many different proteins, including various types of keratins, keratin-associated proteins (KFAPs) and enzymes drawn from animal tissues.
- What is the main ingredient in keratin?
- Keratin is a protein, helical and fiber-like, made of long chains of sulfurised amino-acids (mainly, cysteine and methionine).
- What is the composition of keratin element?
- Keratin is composed of 18 amino acids. The most abundant amino acids are: Cysteine, cystine, serine, glutamic acid, glycine, threonine, arginine, valine, leucine and isoleucine. Alpha keratin, fibrous and with a low sulphur content, is the protein we find in the greatest quantity in hair.
- What materials are in keratin?
- The alpha-keratin filament has a diameter of 7–10 nm while, 3–4 nm for beta-keratin filament [38,39]. Wool keratin has a distinct three-dimensional structure and it contains about 95% of proteins, 0.5% minerals and trace amount of lipids (0.1%) [40,41].
- Is keratin made from biotin?
- Biotin because the two often work hand in hand. Biotin transports oxygen to hard-to-reach hair follicles and the supporting structures. The body uses biotin to synthesize many amino acids, which later transform into keratin.
- What is the composition of keratin?
- This basic (type II) keratin consists of 551 amino acids and 80% of the sequence of these amino acids is the same as in the keratin K5 (Winter et al. 1998). In contrast, the amino acid sequence of K75 is only 74% similar to that of K6a and K6b (Winter et al. 1998).
- Where is keratin found in the body?
- Where is keratin located? Keratin is in your hair, nails and your skin's outer layer, and it's also in your glands and organs.
- What is the function of the keratin?
- What are the functions of keratin? Keratin protects epithelial cells, strengthens the skin, strengthens internal organs, controls the growth of epithelial cells, and maintains elasticity in the skin. It also holds epithelial cells together and helps them combat mechanical stress.
- Is cuticle composed of keratin?
- - the cuticle: a thin, protective outer layer that contains the nourishing part essential to the development of the hair, highly keratinized, composed of scale-like cells that overlap one another, these are about 60 micrometers long and 6 micrometers wide.
- What molecule is keratin?
- Α-keratin is a polypeptide chain, typically high in alanine, leucine, arginine, and cysteine, that forms a right-handed α-helix. Two of these polypeptide chains twist together to form a left-handed helical structure known as a coiled coil.
- What kind of substance is keratin?
- What is keratin? Keratin is a protein that helps form hair, nails and your skin's outer layer (epidermis).
- Is keratin a monomer or polymer?
- Keratins (also described as cytokeratins) are polymers of type I and type II intermediate filaments that have been found only in chordates (vertebrates, amphioxus, urochordates).
- Is keratin a chemical compound?
- In addition to water, the elements that compose the chemical composition of hair are: keratin, lipids, minerals and pigments. Keratin is a protein found in the cortex. Keratin is composed of 18 amino acids.
- What type of tissue contains keratin?
- Keratin exists in different forms like α-keratin and β-keratin. α-Keratin is usually found in soft tissues like sheep wool, skin, and hair, while β-keratin is found in hard tissues like bird feathers, horns, claws, and hooves [77].
- Where is keratin mostly found?
- Where is keratin located? Keratin is in your hair, nails and your skin's outer layer, and it's also in your glands and organs.
- Which part of the body has the most keratin?
- Answer and Explanation: The layer of the skin which contains the most keratin is the epidermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin which is further subdivided into three to five layers.
- What are examples of Keratinized tissue?
- Keratinized epithelium has keratin deposited on the surface which makes it impermeable and dry. Examples of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium include skin, the epidermis of the palm of the hand, and the sole of the foot, and the masticatory mucosa.
- What is keratin and what is its function in the skin?
- What are the functions of keratin? Keratin protects epithelial cells, strengthens the skin, strengthens internal organs, controls the growth of epithelial cells, and maintains elasticity in the skin. It also holds epithelial cells together and helps them combat mechanical stress.
- How is the presence of keratin helpful to skin cells?
- Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress.
- How does keratin in the skin help protect the human body?
- Keratinocytes (pronounced: ker-uh-TIH-no-sites) make keratin, a type of protein that's a basic component of hair, skin, and nails. Keratin in the skin's outer layer helps create a protective barrier. Langerhans (pronounced: LAHNG-ur-hanz) cells help protect the body against infection.
- What is the Keratinization of the skin?
- Keratinization, also termed as cornification, is a process of cytodifferentiation which the keratinocytes undergo when proceeding from their post germinative state (stratum basale) to finally differentiated, hardened cell filled with protein, constituting a structurally and functionally distinct keratin containing
- What is the function of keratin in the skin quizlet?
- What is the function of Keratin? Provides protection against water loss from the body. What structures are embedded in the dermis? Hair, nails, and certain glands.
- What is the keratin layer of epithelium?
- Hear this out loudPauseKeratinized Epithelium The stratum corneum is the outermost layer that is composed of keratinized squamous cells. This keratin forms the outer layer of the skin of reptiles, birds and mammals. These keratinized cells are actually dead cells that shred periodically. They form an effective barrier against abrasions.
- Is keratin found in skin tissue?
- Hear this out loudPauseKeratin is found in the epidermis layer of the skin. The epidermis is the top, outermost layer of skin cells. The skin is the largest organ in the body and serves as a protective layer to internal organs.
- Where is keratin found in the skin quizlet?
- Hear this out loudPauseepidermis contains an outer layer of dead skin cells, the stratum corneum, that forms a tough protective protein called keratin.
- What layer of skin contains keratin?
- Epidermis Your epidermis is the top layer of the skin that you can see and touch. Keratin, a protein inside skin cells, makes up the skin cells and, along with other proteins, sticks together to form this layer.
- Where is keratin found in the skin?
- Epidermis layer Keratin is found in the epidermis layer of the skin. The epidermis is the top, outermost layer of skin cells. The skin is the largest organ in the body and serves as a protective layer to internal organs.
- Which layer is comprised of keratin?
- The Epidermis The Epidermis. The epidermis is composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. It is made of four or five layers of epithelial cells, depending on its location in the body.
- Where is the most keratin found?
- The epidermis Keratin filaments are abundant in keratinocytes in the hornified layer of the epidermis; these are proteins which have undergone keratinization. They are also present in epithelial cells in general.
Keratin is found in what cells
| What is the main purpose of keratin? | Keratin is a protein that helps form hair, nails and your skin's outer layer (epidermis). It helps support your skin, heal wounds and keep your nails and hair healthy. |
| What is the function of the keratin in the epithelium? | A major function of keratin IFs is to protect epithelial cells from mechanical and non-mechanical stresses that cause cell rupture and death. Interference with this role is the root cause of a large number of inherited epithelial fragility conditions. |
| What does it mean when a cell is filled with keratin? | Keratinization, also termed as cornification, is a process of cytodifferentiation which the keratinocytes undergo when proceeding from their post germinative state (stratum basale) to finally differentiated, hardened cell filled with protein, constituting a structurally and functionally distinct keratin containing |
| What does keratin do for hair cells? | Keratin is a cytoskeletal protein that forms intermediate filaments within epithelial cells and participates in maintaining the strength of the cells1. It is a major protein found within the hair that contributes to its mechanical strength2. |
| Where is keratin made in the cell? | Keratin is produced in cells called keratinocytes. These cells are found among other epithelial cells that line the surface of the body. |
| What layer of the skin is keratin found in? | The layer of the skin which contains the most keratin is the epidermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin which is further subdivided into three to five layers. Thick skin has five layers in the epidermis, while thin skin only has three layers. |
| Where is keratin produced in the body? | Keratins produced in the suprabasal cells of the soft-keratinizing and cornifying epidermis of the skin differ from the keratins produced in the suprabasal epithelial cells of the hard-keratinizing and cornifying epidermis of the hair cortex, hair cuticle or plate of the human fingernail. |
| Where does your body get keratin? | The nutrients in certain foods can boost keratin production in the body, helping to strengthen the skin, hair, and nails. Examples of these foods include eggs, salmon, onion, sweet potato, and more. Keratin is a protein that helps maintain the structure of hair, nails, skin, and the lining of the internal organs. |
| Which layer of epidermis has most keratin? | The stratum corneum Answer and Explanation: The epidermis layer that has the most keratinized cells is the stratum corneum. The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis and serves to protect the inner layers of the epidermis from mechanical damage and desiccation. |
| What is a major function of keratin? | A major function of keratin IFs is to protect epithelial cells from mechanical and non-mechanical stresses that cause cell rupture and death. Interference with this role is the root cause of a large number of inherited epithelial fragility conditions. |
| What is the function of the keratin gene? | Normal Function The KRT1 gene provides instructions for making a protein called keratin 1. Keratins are a group of tough, fibrous proteins that form the structural framework of cells called keratinocytes that make up the skin, hair, and nails. |
| Why are the keratin cells important? | As part of the epithelial cytoskeleton, keratins are important for the mechanical stability and integrity of epithelial cells and tissues. Moreover, some keratins also have regulatory functions and are involved in intracellular signaling pathways, e.g. protection from stress, wound healing, and apoptosis. |
| Where is keratin produced in hair? | In the lower portion of the hair cortex, K85 forms keratin filaments with the acidic keratin K31 (Langbein et al. 2007). Keratin K86 (hHb6): K86 has a MW of 53.5 kDa and an isoelectric pH of 5.3; it is produced in the suprabasal cells of the cortex in human hairs (Langbein et al. |
| Where does human keratin come from? | Keratin is a protein that your body produces naturally, and it helps keep your hair, skin and nails healthy and strong. Your body produces keratin naturally, but keratin shampoos and conditioners that contain keratin hydrolysates may strengthen your hair and improve its appearance. |
| What cells produce and store the protein keratin? | The cells in all of the layers except the stratum basale are called keratinocytes. A keratinocyte is a cell that manufactures and stores the protein keratin. Keratin is an intracellular fibrous protein that gives hair, nails, and skin their hardness and water-resistant properties. |
| Where is the protein keratin most likely to be found? | Keratin is the name for a family of structural proteins which are abundant in the outer layer of human skin, in hair, and in nails. |
| What is keratin and where is it found? | Keratin is a type of structural protein found in your hair, skin, and nails ( 1 ). It's especially important for maintaining the structure of your skin, supporting wound healing, and keeping your hair and nails healthy and strong ( 1 ). |
| Where are keratin cells found? | Epidermis layer Keratin is found in the epidermis layer of the skin. The epidermis is the top, outermost layer of skin cells. The skin is the largest organ in the body and serves as a protective layer to internal organs. |
| What epithelial tissue is keratin found in? | Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium that contains numerous layers of squamous cells, called keratinocytes, in which the superficial layer of cells is keratinized. This type of epithelium comprises the epidermis of the skin. |
| What gives keratin to hair? | The nutrients in certain foods can boost keratin production in the body, helping to strengthen the skin, hair, and nails. Examples of these foods include eggs, salmon, onion, sweet potato, and more. Keratin is a protein that helps maintain the structure of hair, nails, skin, and the lining of the internal organs. |
| Where does keratin for hair come from? | Your body produces keratin naturally. Animal fur, feathers, hooves and horns also consist of keratin. The keratin in keratin hair treatments usually comes from ground-up animal parts, so if you're a vegetarian, you may not want to use these products. |
| What stimulates the production of keratin? | 3. Focus on Biotin-rich Diet. Biotin too boosts keratin production by metabolizing amino acids to strengthen hair and nails. A few good sources of biotin are whole grains, eggs (with the yolk), bananas, and a variety of nuts like walnuts, peanuts, pecans, almonds, and more. |
| What is keratin caused by? | Keratin is a tough, fibrous protein found in fingernails, hair, and skin. The body may produce extra keratin as a result of inflammation, as a protective response to pressure, or as a result of a genetic condition. Most forms of hyperkeratosis are treatable with preventive measures and medication. |
| What makes hair grow keratin or biotin? | Keratin for hair health, both compounds offer unique benefits. Biotin is known for promoting hair growth and strength, while keratin contributes to hair resilience and repair. Combining these two elements in a comprehensive hair care routine can lead to luscious and healthy locks. |
| Where is keratin produced in the epidermis? | The Squamous Cell Layer Keratinocytes produce keratin, a tough, protective protein that makes up the majority of the structure of the skin, hair, and nails. The squamous cell layer is the thickest layer of the epidermis, and is involved in the transfer of certain substances in and out of the body. |
| Is keratin intracellular or extracellular? | Intracellular The chief difference between keratins and the underlying connective tissue proteins is that the structural elements of keratins are intracellular, whereas those of connective tissues are extracellular. |
| Where is the keratin layer located? | Epidermis The layer of the skin which contains the most keratin is the epidermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin which is further subdivided into three to five layers. Thick skin has five layers in the epidermis, while thin skin only has three layers. |
| What is the keratin in the epidermis? | Keratins are the major structural proteins of the vertebrate epidermis and its appendages, constituting up to 85% of a fully differentiated keratinocyte. Together with actin microfilaments and microtubules, keratin filaments make up the cytoskeletons of vertebrate epithelial cells. |
| What parts of the body use keratin? | Summary. Keratin is a naturally occurring protein in the body that is found in the hair, skin nails, mouth, and internal organs. It plays a key role in providing structure and protection to the skin and tissues. |
| What causes too much keratin in skin? | Pressure-related hyperkeratosis occurs as a result of excessive pressure, inflammation or irritation to the skin. When this happens, the skin responds by producing extra layers of keratin to protect the damaged areas of skin. Non-pressure related keratosis occurs on skin that has not been irritated. |
| How is keratin produced? | Keratin is produced in cells called keratinocytes. These cells are found among other epithelial cells that line the surface of the body. |
- How do animals produce keratin?
- The horn, hooves, nails, hair, and other keratin-based hard, tough materials growing on animals are produced by epithelial cells adapted to growing an abundance of keratin and then dying as individual cells while leaving the keratin to help form a structure valuable to the whole animal.
- What causes keratin production?
- Keratin is a tough, fibrous protein found in fingernails, hair, and skin. The body may produce extra keratin as a result of inflammation, as a protective response to pressure, or as a result of a genetic condition.
- What organisms have keratin based structures?
- They are found in the nails, scales, and claws of reptiles, in some reptile shells (testudines, such as tortoise, turtle, terrapin), and in the feathers, beaks, and claws of birds.
- What is the function of keratin in tissue?
- Keratin is a protein that helps form hair, nails and your skin's outer layer (epidermis). It helps support your skin, heal wounds and keep your nails and hair healthy.
- What is the importance of keratin in the epithelium?
- A major function of keratin IFs is to protect epithelial cells from mechanical and non-mechanical stresses that cause cell rupture and death. Interference with this role is the root cause of a large number of inherited epithelial fragility conditions.
- What is the importance of keratin in the body?
- What are the functions of keratin? Keratin protects epithelial cells, strengthens the skin, strengthens internal organs, controls the growth of epithelial cells, and maintains elasticity in the skin. It also holds epithelial cells together and helps them combat mechanical stress.
- Which tissue may contain keratin?
- Epidermal tissues Keratin is the major or sole protein in epidermal tissues and appendages including: scales, claws, and beaks (reviewed e.g., Greenwold et al., 2014). Keratins have multiple β-pleated sheets and are therefore resistant to proteolysis.
- What happens if you don't have keratin?
- If your body isn't able to make enough keratin (either because your diet is falling short in protein, key nutrients, or something else is going on), the effects will likely be noticeable in your hair, nails, and skin. Your hair and nails may grow at a slower rate, and become more brittle and less shiny and smooth.
- What kind of molecule is keratin
- By HH Bragulla · 2009 · Cited by 826 — 'Keratin' is often misunderstood to be a single substance, even though it is composed of a complex mixture of proteins, such as keratins, KFAPs and enzymes
- The structure of hair is formed by keratin keratin is most likely which of the following polymers?
- The structure of hair is formed by keratin. Keratin is most likely which of the following polymers? A. nucleic acid B. lipid C. starch D. protein.
- Which tissue does Keratinization occur within?
- Keratinization is defined as cytoplasmic events that take place in keratinocytes that move through the different layers of the epidermis to finally differentiate into corneocytes.
- What is keratin and what is its function?
- What is keratin? Keratin is a protein that helps form hair, nails and your skin's outer layer (epidermis). It helps support your skin, heal wounds and keep your nails and hair healthy. There are 54 kinds of keratin in your body.
- Where do you get keratin from?
- The nutrients in certain foods can boost keratin production in the body, helping to strengthen the skin, hair, and nails. Examples of these foods include eggs, salmon, onion, sweet potato, and more. Keratin is a protein that helps maintain the structure of hair, nails, skin, and the lining of the internal organs.
- What does keratin in the skin look like?
- Keratin plugs are white or skin-colored bumps that develop on the skin. These clogged pores are more common in children and teenagers. They feel rough and often appear in groups on the upper arms and bottom. These bumps are harmless, don't require treatment and usually go away on their own.
- How do you prevent keratin build up?
- While it may be difficult to prevent keratin plugs entirely, you can help get rid of them and prevent others from occurring by:
- Moisturizing your skin regularly.
- Avoiding tight, restrictive clothing.
- Using a humidifier in cold, dry weather.
- Limiting bathing time.
- Using lukewarm water in showers and baths.
- While it may be difficult to prevent keratin plugs entirely, you can help get rid of them and prevent others from occurring by:
- What happens when your body produces too much keratin?
- Keratosis pilaris is caused by the buildup of keratin — a hard protein that protects skin from harmful substances and infection. The keratin blocks the opening of hair follicles, causing patches of rough, bumpy skin. It's not clear why keratin builds up in people with keratosis pilaris.
- Which layer is responsible for keratin production?
- The stratum basale is in the deepest layer of your epidermis. New skin cells develop in this layer. It also contains the keratinocyte (cur-at-in-o-site) stem cells, which produce the protein keratin. Keratin helps form hair, nails and your skin's outer layer, which protect you from the harsh environment.
- Why is my body producing too much keratin?
- Pressure-related hyperkeratosis occurs as a result of excessive pressure, inflammation or irritation to the skin. When this happens, the skin responds by producing extra layers of keratin to protect the damaged areas of skin. Non-pressure related keratosis occurs on skin that has not been irritated.
- What cells make keratin proteins called?
- Keratin is produced in cells called keratinocytes. These cells are found among other epithelial cells that line the surface of the body.
- What is the scientific name for keratin protein?
- Keratins (also described as cytokeratins) are polymers of type I and type II intermediate filaments that have been found only in chordates (vertebrates, amphioxus, urochordates).
- What cells are filled with keratin?
- The keratinised squames layer (stratum corneum) is the final layer. These are layers of dead cells, reduced to flattened scales, or squames, filled with densely packed keratin.
- What is the name of the cells that secrete keratin?
- Keratinocytes are the predominant cell type of epidermis and originate in the basal layer, produce keratin, and are responsible for the formation of the epidermal water barrier by making and secreting lipids.
- Where is keratin found in the cell?
- Epithelial cells Keratin is an intermediate filament that helps hold skin cells together. It is most often found in the epithelial cells of the skin, nails, and hair. Epithelial cells line the surface of the body.
- Where is keratin found in the epidermis?
- Keratin filaments are abundant in keratinocytes in the hornified layer of the epidermis; these are proteins which have undergone keratinization. They are also present in epithelial cells in general.
- Where does keratin production occur?
- Keratins produced in the suprabasal cells of the soft-keratinizing and cornifying epidermis of the skin differ from the keratins produced in the suprabasal epithelial cells of the hard-keratinizing and cornifying epidermis of the hair cortex, hair cuticle or plate of the human fingernail.
- Where is Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
- Keratinized epithelium has keratin deposited on the surface which makes it impermeable and dry. Examples of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium include skin, the epidermis of the palm of the hand, and the sole of the foot, and the masticatory mucosa.
- Where is keratin obtained?
- Your body produces keratin naturally. Animal fur, feathers, hooves and horns also consist of keratin. The keratin in keratin hair treatments usually comes from ground-up animal parts, so if you're a vegetarian, you may not want to use these products.
- What is the location and function of Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
- The stratified squamous keratinised epithelium of the epidermis, which forms the outermost layer of the skin, protects the body against various external influences, such as mechanical stress, radiation, microbial penetra- tion, and exsiccation.
- And what part in the integumentary protein are formed where is protein keratin found
- Jun 9, 2022 — Keratin is a protein that helps form hair, nails and your skin's outer layer (epidermis). It helps support your skin, heal wounds and keep your
- Where is keratin primarily found
- The harder beta-keratins (β-keratins) are found only in the sauropsids, that is all living reptiles and birds. They are found in the nails, scales, and claws

